Phone:+ 86-769-83341628
Fax:+ 86-769-83342028
Email: emeidg@emeigroup.com
Website: http://www.emeigroup.com.cn/

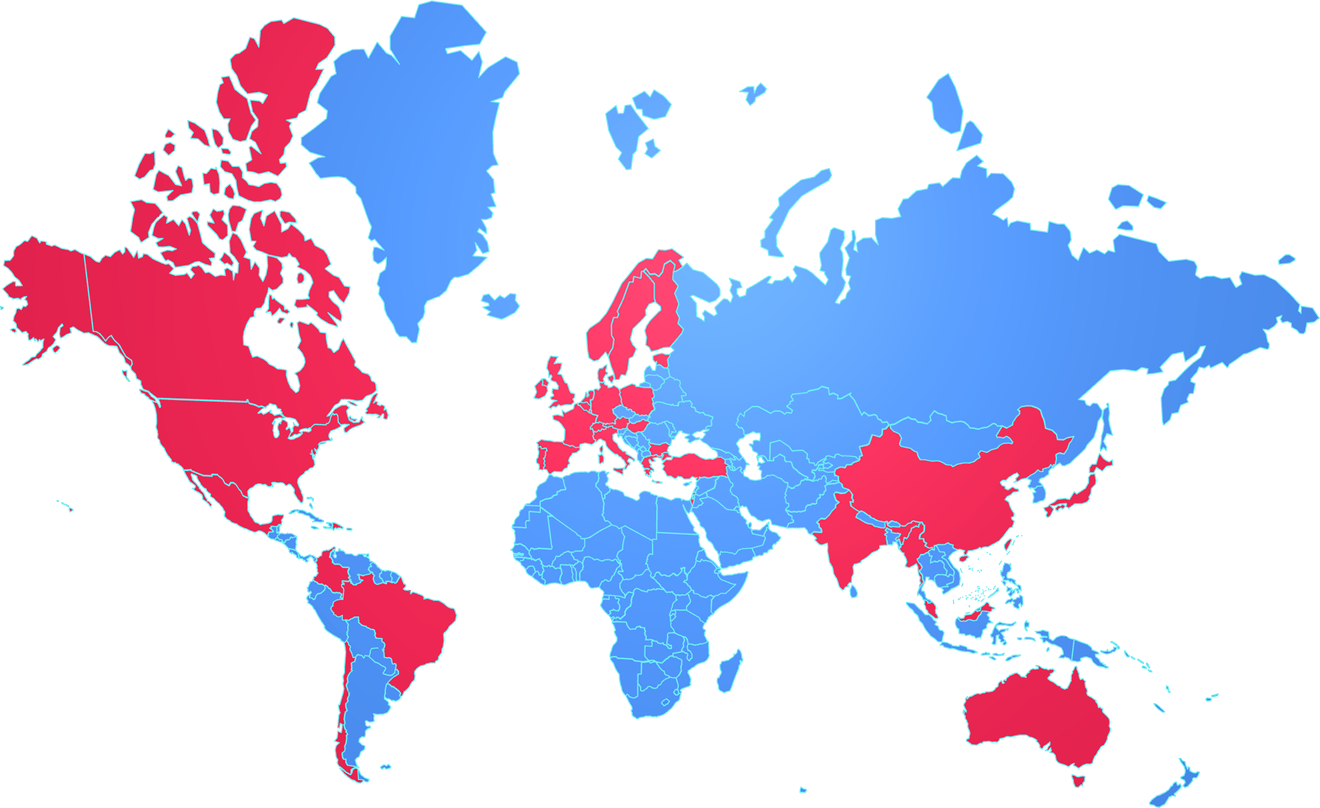
Automotive
Thermal conductive and wave-absorbing materials are widely used in the automotive market, each playing a crucial role in enhancing vehicle performance, ensuring the stable operation of equipment, and improving passenger safety. Below are the specific applications of these two types of materials in the automotive market:
I. Application of Thermal Conductive Materials
Thermal conductive materials are primarily used in the automotive market to improve the heat dissipation efficiency of electronic devices and power systems, ensuring stable vehicle operation even under high-temperature conditions. Specific applications include:
Battery Systems:
In new energy vehicles, power batteries are key components for energy storage and output, generating significant heat during operation. Thermal conductive materials (such as thermal conductive silicone, graphite, etc.) are widely used in the thermal design of battery packs to improve heat dissipation efficiency, prevent overheating, and extend battery life.
Motor and Electronic Control Systems:
Electric vehicle motors and electronic control systems also produce substantial heat during operation. Thermal conductive materials are used to design efficient cooling solutions, such as thermal pads and gels, to ensure the stable operation of motors and electronic control systems.
Onboard Electronic Devices:
Onboard electronic devices such as navigation systems, audio systems, and air conditioning also generate heat during operation. By using thermal conductive materials, these devices can operate normally even in high-temperature environments, improving passenger comfort and safety.
II. Application of Wave-Absorbing Materials
Wave-absorbing materials are primarily used in the automotive market to reduce electromagnetic interference and improve the performance and reliability of automotive electronic devices. Specific applications include:
Electromagnetic Interference Suppression:
Modern vehicles incorporate numerous electronic devices, such as radar, sensors, and wireless communication equipment. These devices generate electromagnetic radiation during operation, which can cause mutual interference. Wave-absorbing materials can effectively absorb these electromagnetic waves, reduce interference, and enhance device performance and stability.
Radar System Optimization:
In autonomous driving and advanced driver-assistance systems, radar is a critical sensing component. Wave-absorbing materials can be applied to radar antenna covers or surrounding structures to reduce radar wave reflection and scattering, improving radar detection accuracy and reliability.
Vehicle Body Electromagnetic Shielding:
While the metal structure of a vehicle body inherently provides some electromagnetic shielding, it may be insufficient in certain cases to fully block external electromagnetic interference. By applying wave-absorbing materials to key areas of the vehicle body, electromagnetic shielding can be further enhanced, protecting onboard electronic devices from external interference.
In summary, thermal conductive and wave-absorbing materials hold broad application prospects and development potential in the automotive market. With the continuous advancement of automotive technology and increasing consumer demands for vehicle performance, the application of these materials will become more extensive and in-depth.